Again within the early 2000s, after I was butting heads seemingly each week with individuals who believed the Apollo moon landings had been faked, such people would pull out an argument they thought was their ace within the gap: If NASA’s Hubble Area Telescope is highly effective sufficient to see the intricate particulars of distant galaxies, why can’t it see the Apollo astronaut boot prints on our personal moon?
Like most conspiratorial pondering, this argument appears persuasive on its floor however falls aside underneath the slightest scrutiny. These taken in by it have a misunderstanding of two issues: how telescopes work and simply how large area is.
Many individuals assume a telescope’s objective is to amplify photos. Definitely producers of cheap (learn: low-cost) telescopes like to market them as such: “150x power!” they print in big lettering on the field (together with extremely deceptive images from a lot larger telescopes). Whereas magnification is vital, a telescope’s actual energy is in its decision, nonetheless. The distinction is refined however essential.
On supporting science journalism
Should you’re having fun with this text, think about supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By buying a subscription you’re serving to to make sure the way forward for impactful tales in regards to the discoveries and concepts shaping our world right now.
Magnification is simply how a lot you possibly can zoom in on an object, making it look larger. That’s vital as a result of whereas astronomical objects are bodily large, they’re very distant, so they seem small within the sky. Magnifying them makes them simpler to see.
Decision, however, is the flexibility to differentiate two objects which are very shut collectively. For instance, you may understand two stars orbiting one another—a binary star—as a single star as a result of they’re too carefully spaced to your eye to separate. You possibly can’t resolve them. Trying by a telescope with greater decision, nonetheless, you may be capable to discern the separation between them, revealing that they’re two particular person stars.
However isn’t that simply magnification, then? No—as a result of magnification solely makes issues larger! That is straightforward to reveal with {a photograph}: you possibly can zoom in on the {photograph} as a lot as you’d like, however previous a sure restrict, you’re simply magnifying the pixels, and you may’t get any extra info out of it. To interrupt by that wall, it’s a must to acquire decision relatively than magnification.
A Hubble Area Telescope picture of the Apollo 17 touchdown area throughout the Taurus-Littrow valley of the moon. This picture lacks the required decision to disclose any signal of the lunar lander or the astronauts’ floor exercise.
NASA/ESA/J. Garvin (NASA/GSFC)
The issue is that decision is inherent to the telescope itself, that means that main boosts in decision normally require upgrading to a a lot larger telescope. However regardless of how large your telescope turns into, it can nonetheless have restricted decision. When the sunshine from an infinitesimally small dot comparable to a distant star passes by a telescope, its mild will get unfold out a little bit bit contained in the telescope optics (the mirrors or lenses). It is a elementary property of sunshine referred to as diffraction, and it may possibly’t be averted.
As I alluded to earlier, the decision of a telescope relies upon partly on the scale of its mirror or lens. The larger the light-gathering optics, the higher the decision. However the best way mild spreads out within the optics depends upon its wavelength, with shorter wavelengths yielding greater decision. So two blue stars shut collectively is likely to be resolvable in a telescope, whereas two purple stars on the similar separation received’t be. When astronomers construct telescopes with cameras on them, they should account for the wavelength they need to observe once they determine how large the digicam pixels can be. In any other case they’re simply magnifying noise, very like our earlier instance of zooming in too far on {a photograph}.
All this results in a shocking outcome. The Hubble Area Telescope has a mirror that’s 2.4 meters vast. NASA’s James Webb Area Telescope (JWST) has a mirror that’s 6.5 meters throughout, so that you’d count on JWST to have a lot greater decision. And at some wavelengths, it does: the shortest wavelength JWST can see is about 0.6 micron (what our eyes understand as orange mild), and there its decision is technically significantly better than Hubble’s.
However JWST is designed to be an infrared telescope. At these wavelengths, say round two microns, its decision is akin to what Hubble can see at seen mild wavelengths. Out within the mid-infrared, at 10 to twenty microns, JWST’s decision is even decrease. Thoughts you, as a result of it’s the biggest infrared telescope ever launched into area, it nonetheless supplies a few of the sharpest views we’ve ever had in these wavelengths!
Astronomers measure decision as an angle on the sky. There are 90 levels from horizon to zenith, and we divide levels into 60 arcminutes per diploma and 60 arcseconds per arcminute. (“Arc” denotes that it’s an angle on the sky.) The moon, for instance, is half a level vast within the sky, which is 30 arcminutes, or 1,800 arcseconds. A telescope’s most decision, then, is the minimal separation that it may possibly distinguish between two objects, expressed as an angle.
At its finest, Hubble’s decision is about 0.05 arcsecond—a very tiny angle! However how a lot element it may possibly see in actual phrases depends upon the goal’s distance and bodily dimension. For instance, 0.05 arcsecond is equal to the obvious dimension of a dime seen from about 140 kilometers away.
That brings us again to the conspiracy theorists and their gripe about recognizing boot prints on the moon. Galaxies are sometimes tens of tens of millions and even billions of light-years from Earth. At these distances, Hubble can resolve objects a couple of light-years throughout—tens of trillions of kilometers—at finest. So whereas it appears like we’re seeing galaxies in nice element in these spectacular Hubble photos, the smallest factor we are able to see remains to be tremendously big.
In the meantime the moon is simply about 380,000 km from us—and from Hubble. At that distance, Hubble’s decision surprisingly limits it to resolving objects no smaller than about 90 meters throughout. So not solely can we not see the astronauts’ boot prints in Hubble photos however we can also’t even see the Apollo lunar landers, which had been solely about 4 meters throughout!
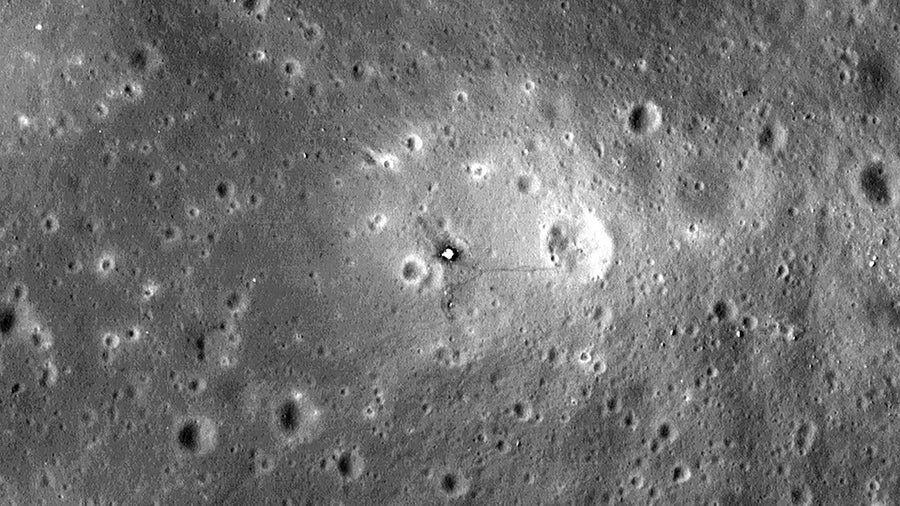

A picture of the Apollo 11 lunar touchdown web site, as captured by NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO). Though the LRO spacecraft makes use of optics a lot smaller than these of the Hubble Area Telescope, its nearer proximity to the lunar floor permits exceptional particulars to be seen, together with the Apollo 11 lander and trails of boot prints from the astronauts.
NASA/Goddard Area Flight Middle/Arizona State College
We are able to see the landers and the boot prints in photos taken by NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, although. Whereas the digicam on this mission has a mirror that’s solely about 20 centimeters vast, the spacecraft is in lunar orbit and has handed over the Apollo touchdown websites at an altitude of solely 50 km. As a result of it’s a lot nearer to the lunar floor, it may possibly see a lot smaller particulars on the moon than Hubble can. That’s why we ship probes to planets: we get significantly better views. Generally there’s no substitute for being there.
The lesson right here is that the best way issues actually work is commonly refined and never what you count on. Claims which may sound affordable disintegrate when a little bit bit extra of the underlying physics. And should you see a telescope that’s marketed primarily based on the machine’s magnification, it’s most likely finest to again away and search for a distinct one. I do know that may be arduous, however you simply want a little bit resolve.