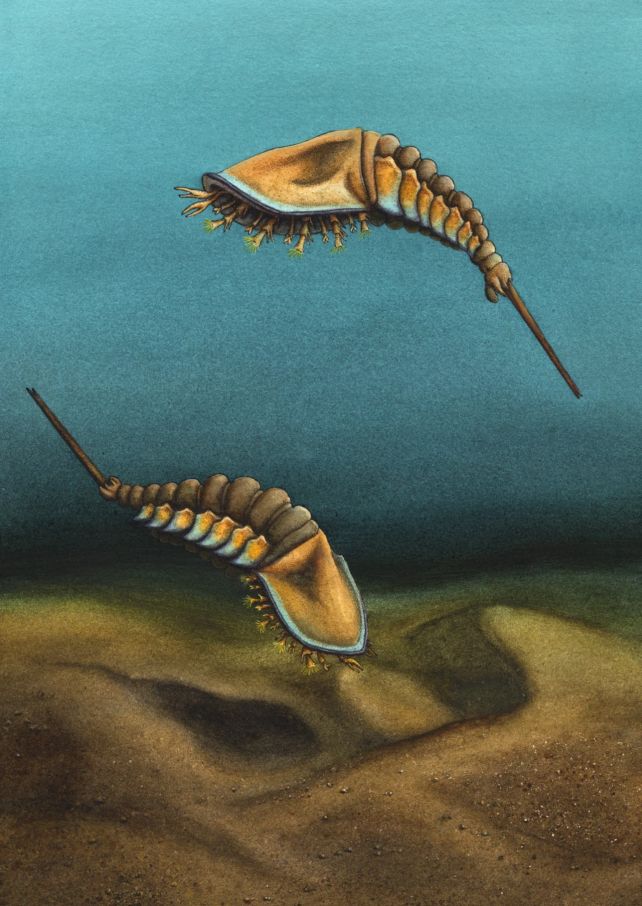
A segmented little beastie that swam Earth’s seas practically half a billion years in the past has now been recognized because the grandparent of spiders, scorpions, and horseshoe crabs.
It is known as Setapedites abundantis, a teeny tiny creature round 5 millimeters lengthy, and it thrived in an ocean that when lined what’s now Morocco, 478 million years in the past.
Now, analyzing its fossils greater than 20 years after they have been first found, paleontologists have realized it belongs to the arthropod clade Euchelicerata.
“Initially, we only intended to describe and name this fossil. We had absolutely no idea that it would hold so many secrets,” says paleontologist Lorenzo Lustri of the College of Lausanne in Switzerland.
“It was therefore an exhilarating surprise to realize, after careful observations and analysis, that it also filled an important gap in the evolutionary tree of life.”
Arthropods are a extremely various and ample group of invertebrates that covers bugs, myriapods, crustaceans, and arachnids – collectively representing round 75 p.c of the world’s animal life. Inside this group, there are subgroups. Chelicerates are arthropods that possess chelicerae – mouthparts formed like fangs or pincers, used to understand and envenom prey.
This group comprises spiders, scorpions, horseshoe crabs, mites, and ticks, in addition to a number of extinct teams, similar to sea scorpions. However we’re not precisely certain when and the way these totally different animals diverged and began on their distinct evolutionary path away from the remainder of the arthropods.
Setapedites abundantis was first unearthed within the early 2000s, in a formation often known as the Fezouata Shale in Morocco. The truth is, it was essentially the most ample sort of fossil within the species, however finding out and characterizing fossils is time-consuming work, and it took a while for researchers to get to it.
Lustri and his colleagues studied a number of fossilized examples of the creature, excellently preserved within the gentle, positive shale that was as soon as silt on the seafloor. And so they discovered anatomical options known as biramous (two-branched) appendages on the animal’s rear.
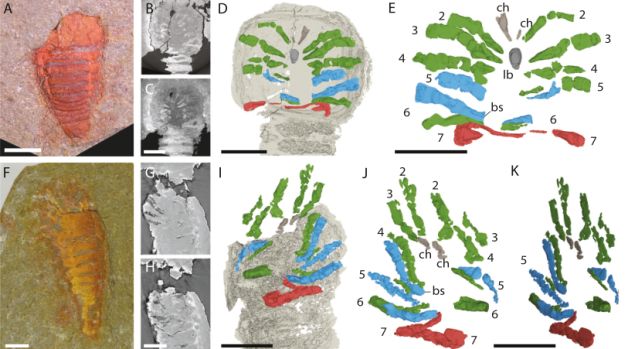
These appendages and their place allowed the researchers to confidently place the species as a member of the household Offacolidae – a genus that features just one different species, Offacolus kingi, which lived throughout the Silurian, between 444 and 420 million years in the past.
Offacolidae are euchelicerates, which signifies that Setapedites abundantis now represents the earliest recognized member of this explicit department of the arthropod household tree, filling the hole between early arthropods and Euchelicerata.
For now, the fossil’s place has been recognized. The subsequent step is to review it additional to raised perceive the emergence and evolution of its distinctive traits, and thus how we got here to have the spiders we all know and love immediately.
The group’s findings have been printed in Nature Communications.



