Magma could be roiling and effervescent simply beneath the floor of Venus, whilst you learn these phrases – and probably breaking by.
A brand new evaluation of knowledge collected over the area of simply eight months within the early Nineties by the Magellan orbiter reveals adjustments within the Venusian floor that may greatest be attributed to volcanism that passed off through the Magellan mission, astronomers have decided.
It is the newest in a sequence of comparable findings – suggesting that volcanic exercise isn’t solely ongoing on Venus, however widespread.
This is a crucial end result. It signifies that any observations we make of Earth’s neighbor and near-twin have to keep in mind the best way volcanism can form the Venusian floor and ambiance – together with the detection of phosphine fuel, interpreted as a possible biosignature, again in 2020.
The end result additionally has relevance when contemplating the evolution of Venus.
A group led by geologist Davide Sulcanese of the Università d’Annunzio in Italy has discovered that Venus has the same volcanic output to Earth over the previous 180 million years, which isn’t solely approach increased than anybody anticipated, however may also help scientists perceive its historical past.
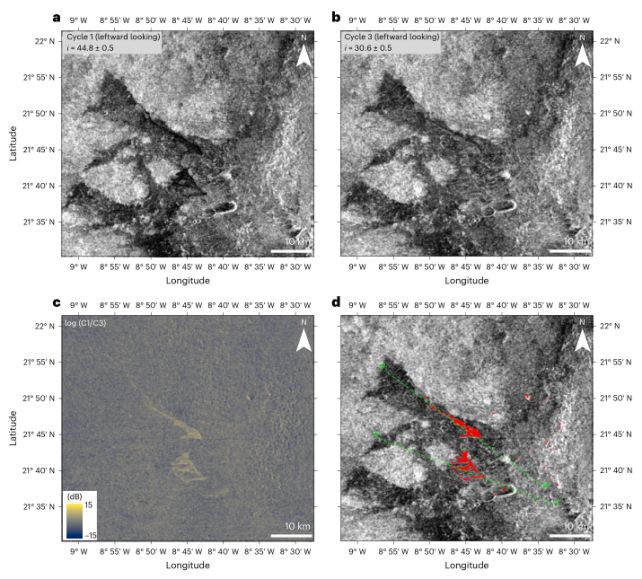
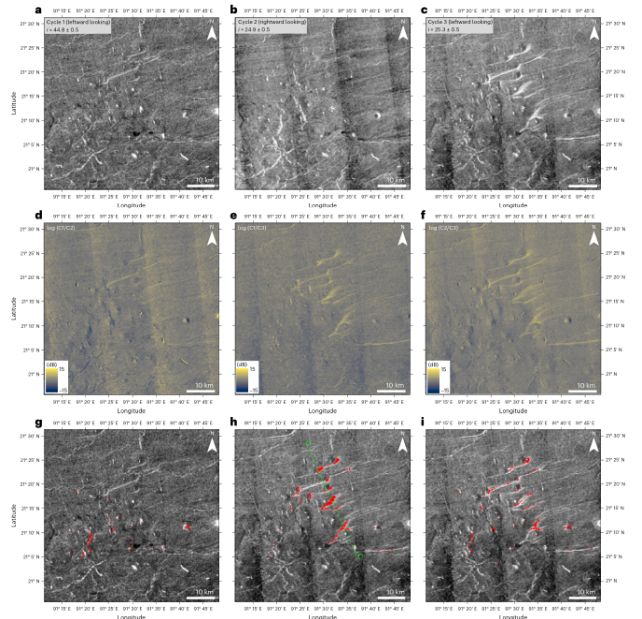
The researchers discovered that the backscatter, or radar reflection sign, modified over time in two completely different volcanic areas as Magellan flew overhead.
frameborder=”0″ allow=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>
“We advise that these adjustments are most moderately defined as proof of recent lava flows associated to volcanic actions that passed off through the Magellan spacecraft’s mapping mission with its synthetic-aperture radar,” the researchers write of their paper.
“This study provides further evidence in support of a currently geologically active Venus.”
Venus, for all its relative proximity to Earth, isn’t effectively understood. We all know a number of issues about it – it has comparable dimension, mass, and mineral composition to Earth, however could be very completely different in different methods.
Its floor temperature and strain are about 30 occasions and 90 occasions these of Earth, respectively. And it is choked by a thick ambiance of principally carbon dioxide that rains sulfuric acid on the bottom under.
Due to these circumstances, Venus isn’t conducive to exploration in the identical approach Mars is, and the thick ambiance makes it very tough to see what’s occurring on the floor.
And there is another downside. Treasured few devoted probes have been despatched to Venus, that means that we merely do not have lots of information from orbit.
However Magellan was geared up with radar that was in a position to penetrate the cloud layer and map the floor under, because it orbited Venus from 1990 to 1994.
Thirty years later, it is nonetheless the perfect info we have now – and, simply final 12 months, scientists revealed that they’d discovered new treasure in that trove. Over an eight-month interval in 1991, a volcanic vent modified form: proof of ongoing volcanic exercise.
By learning a large swath of Magellan information, Sulcanese discovered extra proof of adjustments that passed off in two completely different areas between 1990 and 1992.
On the aspect of a protect volcano known as Sif Mons, and a big volcanic lowland known as the Niobe Planitia, the best way the radar waves mirrored off the floor, or backscatter, modified considerably.
The researchers made an in depth evaluation of those adjustments, and dominated out various explanations comparable to atmospheric results, picture artifacts, or a change within the viewing angle. This allowed them to find out that the probably trigger was a reshaping of the floor as a consequence of lava flows.
With this info in hand, the researchers then set about calculating the amount of volcanic output. They discovered that Sif Mons has a circulation charge of 25.2 and the Niobe Planitia of 37.8 cubic kilometers per 12 months.
Over the previous 180 million years’ Earth’s common volcanic circulation charge has been estimated at 26–34 cubic kilometers per 12 months.
This implies that Venus’ volcanic output could be of the identical order of magnitude as that estimated for Earth.
Final 12 months, scientists posited that Venus may expertise no less than a number of volcanic eruptions per 12 months. This new end result considerably bolsters these findings. However we can’t know for sure till we return there and take a great, lengthy, onerous take a look at Venus.
“In our analysis, we have identified compelling indications of lava flows related to ongoing volcanism in two distinct regions of Venus,” the researchers write. “These findings underscore the importance of continued exploration of Venus.”
Fortunately, there are missions in growth to do exactly that.
The group’s analysis has been printed in Nature Astronomy.