Common bodily exercise can supply main rejuvenation powers, serving to folks retain energy as they age whereas buffering in opposition to sickness and harm. As a rising physique of analysis suggests, this contains beneficial safety all through our our bodies – together with our brains.
In line with a brand new research by researchers from the College of Queensland in Australia, train can gradual and even stop cognitive decline in mice, with a “profound and selective effect” on sure forms of mind cell.
On prime of demonstrating such an intriguing phenomenon in a fellow mammal, the brand new research additionally sheds gentle on how this impact is triggered contained in the brains of bodily energetic mice.
Research have steered comparable advantages for people, however most of the mechanisms driving the consequences stay poorly understood, observe the authors of the brand new research. Analysis like this may yield beneficial insights on precisely how train bolsters the mind.
The researchers examined the consequences of train and growing older on gene expression in particular cell varieties inside the hippocampus, a fancy mind construction concerned with studying and reminiscence.
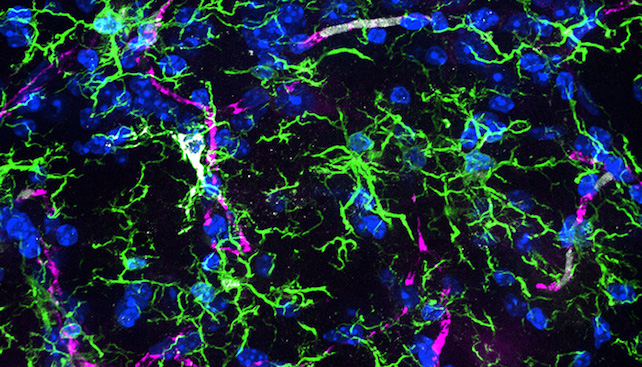
Teams of younger and outdated mice aged 3 or 18 months had been engaged in both sedentary or energetic existence, with the latter getting train by way of a working wheel. Growing old affected all forms of mind cell, however appeared to have an effect on some greater than others, explains research co-author Jana Vukovic.
“We found that aging significantly alters the gene expression of all cell types in the brain, but had greatest impact on the microglia, which are immune cells of the central nervous system that support brain function,” says Vukovic, a neuroimmunologist on the College of Queensland’s Biomedical Sciences and Queensland Mind Institute.
These adjustments aren’t set in stone, nevertheless. When older mice exercised, the research discovered, their microglia regarded extra like these of youthful mice.
“Our research showed that exercise, in the form of a running wheel for the mice, reverted the gene profile of aged microglia to patterns seen in younger versions of the microglial cells,” Vukovic says.
Whereas growing older broadly affected different forms of mind cells to some extent, train elicited a narrower counteracting impact on them, notes lead creator Solal Chauquet, from the College of Queensland’s Institute for Molecular Bioscience.
“Microglia were the only type of brain cell that showed a significant reversal of changes brought about by aging,” Chauquet says.
Together with numerous adjustments in mind cells attributable to growing older, older mice additionally had larger ranges of T cells of their hippocampus, the research discovered.
T cells are white blood cells with massive duties concentrating on overseas intruders, however the researchers aren’t fairly certain why they had been extra prevalent within the brains of older mice.
Nonetheless, bodily exercise was related to a lower on this age-related surge of T cells, hinting at one other doable avenue for train to counteract the consequences of growing older.
“Giving the mice access to a running wheel prevented or reduced the presence of T cells in the hippocampus, a part of the brain involved with memory and learning, during aging,” Vukovic says. “This shows that exercise reduces a process associated with aging in mice.”
Whereas a mouse research can merely trace at potential advantages for folks, this nonetheless supplies an necessary service, Vukovic provides. Future research might depend on findings like these to uncover new insights about our brains, a few of which could in the future assist us evade outdated age somewhat longer.
“Our findings in mice provide a platform for research into the human brain and aging,” she says. “Further research could eventually develop therapeutic ways to target specific cell types to combat aging of the brain.”
The research was revealed in Growing old Cell.