In take a look at pictures of distant galaxies, an array of Occasion Horizon Telescopes has achieved the very best decision observations ever taken from Earth.
It is an achievement that locations inside our grasp much more spectacular pictures of supermassive black holes, providing future enhancements which are 50 % extra detailed than the photographs obtained so far – these of M87*, a supermassive black gap 55 million light-years away, and Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*), the supermassive black gap on the middle of our personal galaxy.
Taken utilizing only a few of the telescopes that make up the Occasion Horizon Telescope (EHT) array, the brand new observations have not resulted in any new pictures. For that, the complete would possibly of the complete array is required.
However the experiment has succeeded in observing the Universe within the most interesting decision ever attained from Earth’s floor, detecting far distant infrared mild at a comparatively increased frequency of 345 GHz, which has a wavelength of simply 0.87 millimeters.
“With the EHT, we saw the first images of black holes using the 1.3-millimeter wavelength observations, but the bright ring we saw, formed by light bending in the black hole’s gravity, still looked blurry because we were at the absolute limits of how sharp we could make the images,” says astrophysicist Alexander Raymond of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
“At 0.87 mm, our images will be sharper and more detailed, which in turn will likely reveal new properties, both those that were previously predicted and maybe some that weren’t.”
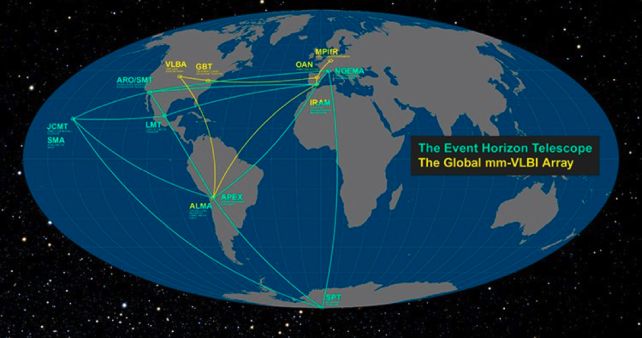
The pictures of M87* and Sgr A* are the product of a method referred to as very lengthy baseline interferometry, or VLBI, involving not one however many radio telescope arrays all over the world, all working along with synchronized precision.
Combining quite a few arrays successfully leads to a collecting-area the dimensions of Earth; the extra telescope antennas used, the extra detailed the ensuing knowledge. However with that many telescopes, there may be a whole lot of knowledge – sorting by means of it, analyzing it, and processing it to supply a picture of the occasion horizon of a black gap is a monumental process. Between the information assortment and the evaluation and processing, every picture takes dedication, time, and labor.
However, the photographs themselves are nonetheless fairly blurry, and there are solely two methods to enhance the decision. The primary is to extend the dimensions of the telescope. That is not going to occur in a rush – the EHT is already Earth-sized. The opposite is observing at the next frequency.
frameborder=”0″ allow=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>
This latter possibility is far more attainable, however not with out its challenges. For instance, water vapor absorbs waves at 0.87 millimeters far more than it does at 1.3 millimeters, leading to a lot increased atmospheric opacity at that wavelength. Earlier 0.87-millimeter observations have required using an area telescope, which does not have the Earth-sized gathering space of the EHT.
The EHT collaboration has developed a option to appropriate for the consequences of water vapor within the environment that improves the effectivity of the array, and permits 0.87-millimeter observations to be taken from the floor of Earth.
The brand new observations promise a decision equal to observing a bottle cap on the Moon from Earth, which implies we might be able to see smaller, fainter, and extra distant supermassive black holes.
The observations additionally imply we might quickly be seeing multi-color views of the recent, roiling materials that swirls round these cosmic behemoths, by imaging in each the 1.3-millimeter and 0.87-millimeter wavelengths concurrently.
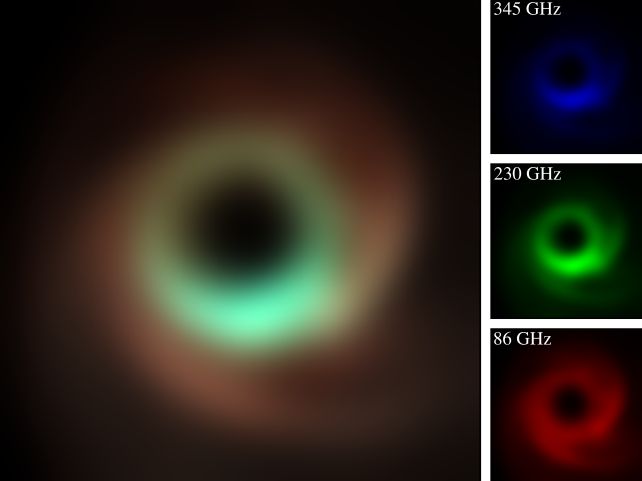
“To understand why this is a breakthrough, consider the burst of extra detail you get when going from black and white photos to color,” says astrophysicist Sheperd ‘Shep’ Doeleman of the Harvard & Smithsonian Heart for Astrophysics and the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory.
“This new ‘color vision’ allows us to tease apart the effects of Einstein’s gravity from the hot gas and magnetic fields that feed the black holes and launch powerful jets that stream over galactic distances.”
We’re very near studying a lot extra about black holes than we have ever been in a position to earlier than. Watch this house – epic science lurks on the occasion horizon.
The analysis has been printed in The Astronomical Journal.