Most want no reminder that motherhood is constrained by a organic clock – it is a undeniable fact that retains many ladies awake at night time, governs profession and relationship selections, and contributes a lion’s share to the US$819 million IVF trade.
However mature fatherhood comes with its personal dangers, and a new examine finds the proportion of US fathers aged 50 or older on the time of their kid’s start is on the rise, which means extra youngsters are more likely to be impacted.
The explanations for this pattern are unclear, however Stanford College urologist Albert Ha and colleagues observe it is usually attributed to “diminished concerns of the male ‘biological clock’ and the desire for educational and financial stability prior to starting a family.”
“Previous studies have also highlighted the influence of evolving gender norms that promote active parental involvement while emphasizing traditional roles like the male ‘breadwinner’,” the authors add.
In a world the place the main focus is normally squarely on the mom, the researchers are involved that public consciousness of those “modest but significant” dangers related to superior paternal age (APA) is missing.
A 2018 examine recognized lots of the dangers of mature fatherhood, utilizing information from 2007 to 2016 for greater than 40 million reside births within the US.
The info revealed that infants born to fathers over the age of 35 have been at greater danger for adversarial outcomes like low start weight, seizures, and respiratory issues instantly after start.
And the older a father was, the higher the chance – for a person aged 45 years or older, his child was 14 p.c extra more likely to be born prematurely, and for a person aged 50 or older, his baby was 28 p.c extra liable to being admitted to neonatal intensive care.
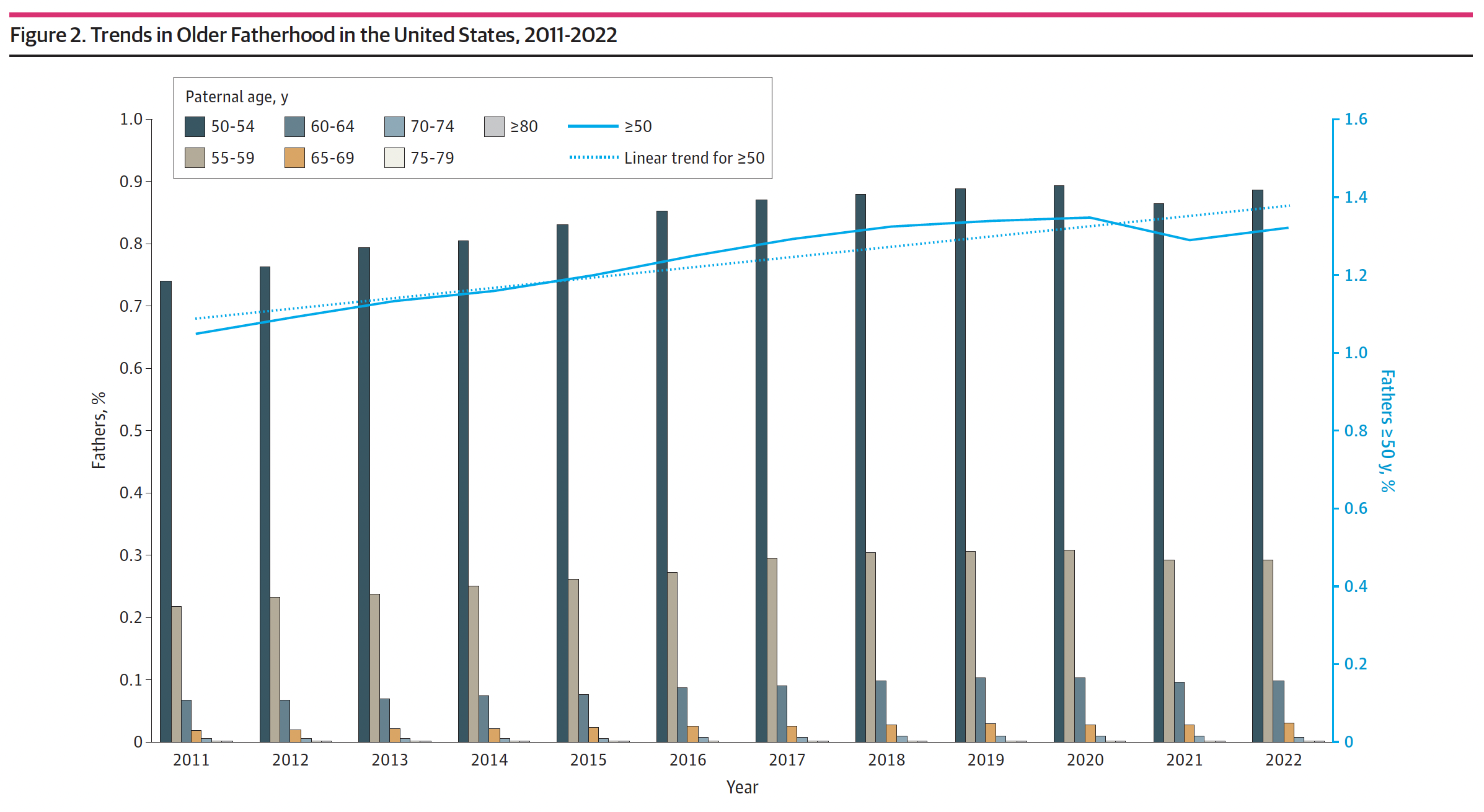
Ha and colleagues analyzed the greater than 46 million reside births reported within the US from 2011 to 2022. Their cross-sectional examine highlights that the proportion of US households affected by these dangers is rising as extra males choose in to parenthood at a mature age.
The typical paternal age rose steadily from 30.8 years in 2011 to 32.1 years in 2022, and the proportion of births involving fathers aged 50 or older elevated from 1.1 p.c in 2011 to 1.3 p.c in 2022. It is a small however vital uptick.
“Recent socioeconomic and demographic trends have shifted the timeline for family building in the US, with many couples increasingly delaying parenthood,” Ha and colleagues write.
Even after controlling for maternal age and different components, each 10-year enhance within the father’s age elevated the proportion of births that relied on assisted reproductive expertise (ART). It was additionally related to a better probability of being the mom’s first start, and an elevated danger of preterm start and low start weight in comparison with fathers aged 30 to 39.
“Paternal age has also affected fertility, pregnancy trajectory, and child health,” the authors write.
“Age-related conditions, such as erectile dysfunction and hypogonadism, impair paternal fecundity, while older age is associated with decreased semen volume, motility, and morphology.”
Analysis has additionally linked older paternal age to declines in sperm high quality, which means the squiggly little gene packets that contribute half of a child’s DNA usually tend to be affected by DNA fragmentation, irregular chromosome numbers, new mutations, and epigenetic alterations.
“Overall, the accumulation of alterations in older men may increase the risk of conditions like autism, pediatric cancers, achondroplasia, and schizophrenia; decrease likelihood of ART success; and heighten risk of perinatal complications,” the authors write.
There have been no vital variations present in toddler intercourse ratio primarily based on a father’s age, besides amongst fathers aged 70 years or older, who have been extra more likely to have a feminine child.
Finally, the analysis highlights the necessity for higher consciousness of the dangers of mature fatherhood, and additional investigation into the components driving this societal shift.
This analysis is printed by JAMA Community Open.