The sunshine of a supernova that has traveled for 10 billion years to succeed in us has given us a brand new measurement of the Hubble fixed – the accelerating charge at which the Universe is increasing.
Known as SN H0pe, it is probably the most distant Kind Ia supernovae we have ever seen, and measurements of the speed at which it appears to be receding have given a Hubble fixed of 75.4 kilometers per second per megaparsec.
This leaves us in a dilly of a pickle. Measures of the early Universe based mostly on a unique methodology known as a ‘normal ruler’ are inclined to return slower outcomes of round 67 kilometers per second per megaparsec.
Whereas SN H0pe seems because it did an entire 4 billion years after the Large Bang, it is a lot additional again in time than different ‘normal candle’ measurements taken within the close by Universe, that are round 73 kilometers per second per megaparsec – suggesting that the stress is constant all through the seen Universe, so far as we will see.
This takes one attainable rationalization for the stress off the desk: that native house is receding at the next charge than distant house. If one approach will get the identical outcomes for each the distant and native Universe, that means that H0 is kind of uniform.
frameborder=”0″ allow=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>
OK, we will clarify. The entire downside is that this factor referred to as the Hubble rigidity – an unresolved discrepancy between the outcomes of various strategies used to measure the accelerating growth of the Universe.
The usual ruler strategy makes use of relics of the early Universe. These are issues just like the cosmic microwave background, or fossilized densities within the distribution of galaxies referred to as baryon acoustic oscillations.
Customary candles, however, are objects of identified intrinsic brightness, resembling Cepheid variable stars, and Kind Ia supernovae. Since these objects are presumed to emit a comparatively constant quantity of sunshine, we will work out how distant they’re by measuring their obvious brightness.
However their usefulness is proscribed by their distance – sooner or later, they develop into too distant to see, so that they’re sometimes solely used to measure the Hubble fixed within the native Universe.
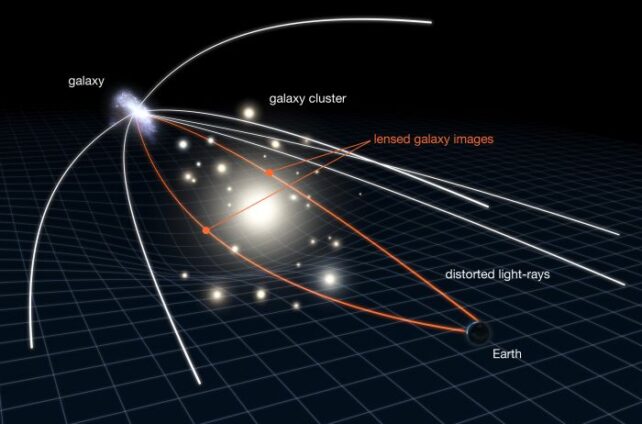
H0pe is loads farther than most Kind Ia supernovae we will see. That is as a result of it is magnified and triplicated by a quirk of space-time often called a gravitational lens.
Round an enormous object, resembling a galaxy or galaxy cluster, space-time tends to curve; any gentle touring by means of this curvature could be repeated and magnified, very similar to curved glass magnifies no matter is behind it.
H0pe, as we defined final 12 months when the invention was made, sits behind a galaxy cluster. As the sunshine from the supernova traveled by means of the gravitational lens generated by the cluster, it magnified and cut up into three distinct dots.
“This is similar to how a trifold vanity mirror presents three different images of a person sitting in front of it. In the Webb image, this was demonstrated right before our eyes in that the middle image was flipped relative to the other two images, a ‘lensing’ effect predicted by theory,” says cosmologist Brenda Frye of the College of Arizona.
“To attain three photographs, the sunshine traveled alongside three totally different paths. Since every path had a unique size, and lightweight traveled on the similar velocity, the supernova was imaged on this Webb statement at three totally different instances throughout its explosion.
“In the trifold mirror analogy, a time-delay ensued in which the right-hand mirror depicted a person lifting a comb, the left-hand mirror showed hair being combed, and the middle mirror displayed the person putting down the comb.”

This allowed the researchers to make an in depth measurement of the Hubble fixed within the distant Universe utilizing a normal candle approach normally solely utilized to the native Universe. The results of 75.4 kilometers per second per megaparsec might not resolve the stress, but it surely does slim down what the reason may be.
The Hubble rigidity is likely one of the greatest issues in cosmology. It is not remotely trivial: it would inform us how large and previous the Universe is, and provides us extra correct measurements throughout space-time as an entire.
Astronomers usually use a Hubble fixed of round 70 kilometers per second per megaparsec to find out distances to cosmic objects – which is simply an estimate based mostly on one of the best knowledge we presently have.
Resolving the Hubble rigidity will doubtless be a Nobel-winning achievement. And the excellent news is that we appear to be getting nearer.
Gravitational waves have given us a brand new instrument to attempt to slim it down – the usual siren. Customary siren measurements have been made; they’re within the neighborhood of each normal rulers and normal candles, so nonetheless inconclusive, but it surely’s solely a matter of time now.
And some extra observations from the JWST might get us there. With simply 4 extra occasions like H0pe, the boldness degree of the measurement might be improved to over three sigma. That will likely be day.
The report of the brand new measurement has been submitted to The Astrophysical Journal, and is out there on preprint server arXiv.