Physicists are one step nearer to nutting out an entire mathematical concept for predicting how blood and different peculiar fluids stream. These weird behaviors have puzzled researchers for many years.
Not that we have tried, however blood truly deforms barely when nudged, and unusually, it thickens up when a powerful, sudden pressure is utilized – shifting from a skinny, watery substance to a extra viscous, nearly stable one.
One other (extra hygienic) instance of that is the basic trick you would possibly keep in mind from faculty science demonstrations: cornstarch combined with water. When you stir it slowly, nothing seems untoward, however squeeze a handful of the combination, and it solidifies right into a rubbery ball. Open your hand, and it will drip like liquid once more.
What’s truly occurring is an instance of a non-Newtonian fluid, a kind of fluid that disobeys Newton’s regulation of viscosity and is as an alternative characterised by its odd relationship between stress, the forces utilized to the liquid, and pressure, the way it deforms in response.
However that is not the one bizarre factor about non-Newtonian fluids. In addition they show a very chaotic fluid movement known as elastic turbulence that exists solely in these fluids, not obedient Newtonian ones.
Turbulence, of any sort, turns an in any other case orderly laminar stream right into a chaotic, churning mess that in industrial settings, makes mixing or pumping fluids tough – or a ship journey on a fast-flowing river bumpy.
It normally occurs at excessive stream speeds, and though it might be a well-recognized phenomenon, describing turbulence in its varied types “remains one of the last unsolved problems in classical physics,” proclaim the researchers behind this new research of elastic turbulence.
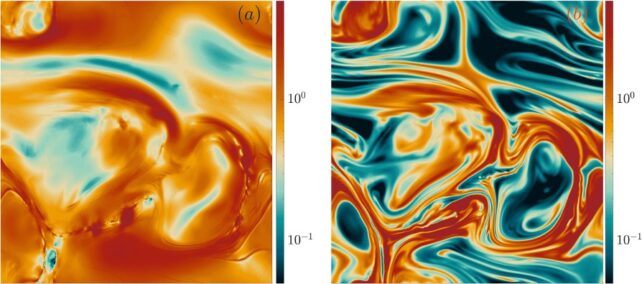
Researchers realized within the Nineteen Nineties that in watery options containing polymers – that are lengthy, repeating chains of molecules – the elasticity of the polymers stretching and contracting triggered laminar flows to change into unstable.
In the beginning of the twenty first century, they found elastic turbulence, which is much more dramatic, rising in gradual laminar flows which can be normally clean.
Elastic turbulence is believed to come up in non-Newtonian fluids, which include ultra-fine particles, polymers, or microscopic cells suspended in watery liquids, from the way in which these particles work together and transfer. With out particles within the resolution, the phenomenon disappears.
Scientists had thought that elastic turbulence was totally totally different from the basic turbulence of Newtonian fluids, which behave in a way more predictable method. However the two phenomena might need extra in frequent than beforehand thought, in accordance with the crew’s new modeling.
Led by Marco Rosti, an aeronautical engineer finding out fluid dynamics on the Okinawa Institute of Science and Know-how in Japan, the crew measured the speed of non-Newtonian fluid flows and calculated the distinction at three factors, not the standard two used to measure and research classical turbulence.
They found that non-Newtonian fluids with elastic turbulence show intermittent fluctuations in velocity at gradual stream speeds, like Newtonian fluids do at excessive flows – a discovering that helped them make statistical predictions about how the non-Newtonian fluid behaved.
“Our results show that elastic turbulence has a universal power-law decay of energy and a so far unknown intermittent behavior,” explains Rosti. “These findings allow us to look at the problem of elastic turbulence from a new angle.”
The research provides to different analysis efforts the place physicists have been making strides in describing non-Newtonian fluids, which have puzzled researchers with their unusual properties for the reason that Nineteen Thirties – after they did not have the devices or computer systems to measure and simulate fluid flows like we do right this moment.
In 2019, researchers at Massachusetts Institute of Know-how (MIT) developed a 3D mannequin that might describe how ultrafine-particle suspensions, like a cornstarch combination, flip from a liquid to a stable and again once more, below varied circumstances.
The economic purposes of such a mannequin are fairly helpful, permitting researchers to foretell and optimize the habits of slurries as they stream between vats in industrial crops, for instance.
frameborder=”0″ allow=”accelerometer; autoplay; clipboard-write; encrypted-media; gyroscope; picture-in-picture; web-share” referrerpolicy=”strict-origin-when-cross-origin” allowfullscreen>
The brand new mannequin developed by Rosti’s crew may have equally sensible makes use of.
“With a perfect theory” – if such a factor exists – “we could make predictions about the flow and design devices that can alter mixing of liquids,” says Rosti. “This might be useful when working with biological solutions,” akin to donated blood and lymph fluid.
Or, when the remainder of us are mucking round with ketchup, custard, and toothpaste – three different enjoyable examples of non-Newtonian fluids.
The research has been revealed in Nature Communications.