T cells, or T lymphocytes, are a cornerstone of the adaptive immune system, integral to defending the physique in opposition to a variety of threats together with infections, most cancers, and different dangerous entities. These specialised white blood cells are crucial for recognizing and responding to particular antigens. They originate from hematopoietic stem cells within the bone marrow and mature within the thymus earlier than circulating by means of the lymphatic system and bloodstream. Understanding T cells’ complicated features and roles within the immune system offers insights into their important contributions to well being and illness.
T Cell Maturation
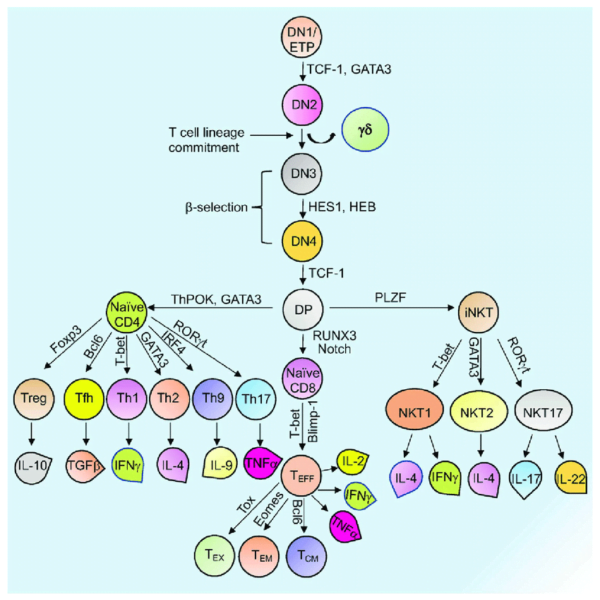
T cells start their journey within the bone marrow, the place hematopoietic stem cells give rise to progenitor T cells. These progenitors then migrate to the thymus, a specialised immune organ, to endure a rigorous maturation course of. Throughout their time within the thymus, T cells develop T cell receptors (TCRs) which can be important for recognizing particular antigens. The maturation course of contains each optimistic and detrimental choice to make sure that T cells can distinguish between self and non-self antigens. T cells that strongly react to self-antigens are usually eradicated, whereas these that may acknowledge international antigens are allowed to mature.
Sign One: Antigen Recognition
Upon leaving the thymus, mature T cells flow into by means of secondary lymphoid organs comparable to lymph nodes and the spleen, trying to find their particular antigen. Preliminary activation happens when T cells acknowledge an antigen offered by Main Histocompatibility Complicated (MHC) molecules on the floor of antigen-presenting cells (APCs).
- CD4+ Helper T Cells: These cells acknowledge antigens offered by MHC class II molecules. The TCR binds to the antigen-MHC class II complicated, and CD4 molecules on the T cell stabilize this interplay by binding to the MHC class II molecule.
- CD8+ Cytotoxic T Cells: These cells acknowledge antigens offered by MHC class I molecules. The TCR binds to the antigen-MHC class I complicated, with CD8 molecules on the T cell offering further stabilization.
This antigen recognition usually takes place in secondary lymphoid organs, the place T cells are primed to reply to particular threats.
Sign Two: Co-Stimulation
For full activation, T cells require further indicators past the antigen-MHC interplay. These secondary indicators guarantee a sturdy and controlled immune response:
- Helper T Cells: CD28 on the T cell binds to B7.1 (CD80) or B7.2 (CD86) on the APC, offering the mandatory co-stimulatory sign for T cell activation. This interplay promotes T cell proliferation and survival. To stop extreme immune responses, CD28 stimulation results in the manufacturing of CTLA-4 (CD152), which competes with CD28 for binding to B7 molecules and modulates the immune response.
- Cytotoxic T Cells: Whereas much less depending on CD28, cytotoxic T cells additionally require indicators from different co-stimulatory molecules comparable to CD70 and 4-1BB (CD137).
Moreover, T cells obtain survival indicators from molecules like ICOS, 4-1BB, and OX40. These are expressed solely after pathogen recognition, guaranteeing that T cells are activated solely by APCs which have encountered and responded to pathogens. Within the absence of those indicators, T cells turn out to be anergic, stopping inappropriate activation.
Sign Three: Cytokine Signaling
After receiving the antigen-specific and co-stimulatory indicators, T cells obtain additional directions within the type of cytokines. These cytokines information the kind of immune response the T cells will mount:
- Helper T Cells: The cytokine atmosphere directs the differentiation of helper T cells into numerous subsets:
- Th1 Cells: Induced by IL-12, these cells improve mobile immunity and are efficient in opposition to intracellular pathogens.
- Th2 Cells: Induced by IL-4, these cells assist fight extracellular pathogens and are concerned in allergic responses.
- Th17 Cells: Induced by IL-6 and IL-23, these cells play a job in inflammatory responses and safety in opposition to sure extracellular pathogens.
These differentiated T cells then migrate to the websites of an infection or irritation. Native cells on the web site, comparable to neutrophils and mast cells, launch further cytokines and chemokines, additional activating and recruiting T cells.
Sorts of T Cells
- Helper T Cells (CD4+ T Cells):
- Perform: Helper T cells coordinate the immune response by releasing cytokines that stimulate different immune cells, together with B cells and cytotoxic T cells.
- Activation: These cells bind to antigens offered by MHC class II molecules on antigen-presenting cells (APCs).
- Cytotoxic T Cells (CD8+ T Cells):
- Perform: Cytotoxic T cells straight kill contaminated or cancerous cells by inducing apoptosis.
- Activation: They acknowledge antigens offered by MHC class I molecules and destroy the goal cells.
- Regulatory T Cells (Tregs):
- Perform: Regulatory T cells assist preserve immune system steadiness by suppressing extreme immune responses and stopping autoimmune reactions.
- Activation: They modulate immune exercise and stop assaults on wholesome tissues.
- Reminiscence T Cells:
- Perform: After an immune response, some T cells turn out to be reminiscence cells that persist within the physique. They “remember” earlier pathogens and permit the immune system to reply extra quickly and successfully upon re-exposure.
How T Cells Work
- Antigen Presentation:
- APCs current antigens on their floor by way of MHC molecules. The kind of MHC (class I or II) determines whether or not a helper or cytotoxic T cell shall be activated.
- T Cell Activation:
- T cells possess distinctive receptors (TCRs) that bind to the antigen-MHC complicated. This binding ensures that T cells are appropriately activated to focus on particular pathogens.
- Clonal Growth:
- Upon activation, T cells endure clonal enlargement, producing quite a few copies of themselves to fight the pathogen successfully.
- Effector and Reminiscence Features:
- Activated T cells, referred to as effector cells, work to eradicate the pathogen. Publish-infection, reminiscence T cells persist to offer long-term immunity.
Places and Maturation
- Bone Marrow: T cells originate from hematopoietic stem cells within the bone marrow.
- Thymus: T cells migrate to the thymus for maturation, the place they endure choice to make sure they’ll acknowledge MHC molecules and differentiate self from non-self.
- Lymph Tissue and Bloodstream: Mature T cells flow into by means of lymphatic tissues such because the spleen, lymph nodes, and tonsils, and likewise within the bloodstream, remaining on standby to reply to pathogens.
Situations and Problems Affecting T Cells
- Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia (ALL): A sort of most cancers that begins within the bone marrow and impacts T cells. It results in an overproduction of immature lymphocytes, which impairs the manufacturing of regular blood cells.
- Hodgkin Lymphoma: A most cancers of the lymphatic system involving T cells. It’s characterised by the presence of Reed-Sternberg cells and might have an effect on lymph nodes and different organs.
- T-Cell Lymphomas: A various group of cancers that originate in T cells and might have an effect on numerous tissues. These embody peripheral T-cell lymphomas and cutaneous T-cell lymphomas.
- DiGeorge Syndrome: A genetic dysfunction ensuing from a deletion on chromosome 22, resulting in underdeveloped or absent thymus. This situation impairs T cell manufacturing and performance.
- HIV/AIDS: HIV primarily targets and destroys helper T cells (CD4+ T cells), resulting in a compromised immune system and development to AIDS if untreated.
- Autoimmune Problems: Situations the place T cells mistakenly assault the physique’s personal tissues, comparable to in a number of sclerosis (attacking the central nervous system) and sort 1 diabetes (attacking insulin-producing cells within the pancreas).
Testing and Monitoring
- T Cell Rely:
- Measures the variety of T cells within the blood. Regular ranges differ by kind and laboratory, with CD4 counts usually between 500 to 1,200 cells/mm³ and CD8 counts between 150 to 1,000 cells/mm³.
- CD4 to CD8 Ratio:
- Assesses the steadiness between helper and cytotoxic T cells. An irregular ratio can point out immune system points, comparable to in HIV an infection the place CD4 counts are low.
- Particular Exams:
- For people with HIV, monitoring T cell counts is essential for assessing immune perform and remedy efficacy. Specialised assessments could embody stream cytometry to research T cell subsets and their perform.
Enhancing T Cell Well being
To help T cell perform and general immune well being:
- Balanced Eating regimen:
- Consuming a wide range of vitamins, together with nutritional vitamins A, C, D, and E, in addition to minerals like zinc and selenium, helps immune perform and T cell well being.
- Common Train:
- Participating in average bodily exercise enhances circulation and general immune perform, contributing to more healthy T cells.
- Enough Sleep:
- Goal for 7-8 hours of high quality sleep per evening to make sure correct immune perform and T cell regeneration.
- Vaccinations:
- Maintaining with beneficial vaccines helps stop infections that might in any other case problem the immune system and T cells.
- Keep away from Dangerous Substances:
- Limiting alcohol and avoiding smoking and vaping assist preserve a wholesome immune system and help T cell perform.
- Hygiene:
- Common hand washing and utilizing hand sanitizer can stop infections and scale back the burden on the immune system.
T Cell Analysis and Isolation
Superior strategies, comparable to microbubble know-how, are revolutionizing T cell analysis and remedy. These strategies enable researchers to isolate and examine T cells with excessive precision. This analysis is pivotal for:
- Gene Expression Research:
- Investigating T cell conduct and performance on the molecular degree offers insights into how T cells reply to infections and different stimuli.
- Vaccine Growth:
- Evaluating T cell responses to new vaccines helps within the improvement of simpler immunizations.
- Adoptive T Cell Remedy:
- This remedy entails enhancing T cells within the lab for remedy of most cancers and different illnesses. Modified T cells are reintroduced into the affected person to focus on and destroy most cancers cells or different pathogens.
Conclusion
T cells are indispensable parts of the immune system, important for combating infections, regulating immune responses, and offering long-term immunity. Their complicated roles contain recognizing particular antigens, present process maturation and activation, and sustaining immune system steadiness. Understanding T cells’ features, sorts, and related issues is essential for advancing medical analysis and bettering therapies. Continued analysis into T cell biology and know-how holds promise for brand spanking new therapeutic methods and higher administration of assorted circumstances.
References
- Janeway, C. A., Travers, P., Walport, M., & Shlomchik, M. J. (2001). Immunobiology: The Immune System in Well being and Illness (fifth ed.). Garland Science.
- Miller, J. F. A., & Matzinger, P. (2002). “The role of T cells in the immune response.” Immunity, 16(1), 1-12. DOI: 10.1016/S1074-7613(02)00004-4
- Dudley, M. E., & Rosenberg, S. A. (2003). “Adoptive cell therapy for cancer: a review.” Immunological Opinions, 193, 50-63. DOI: 10.1034/j.1600-065x.2003.00075.x
- Germain, R. N. (2002). “T-cell development and the role of antigen presentation.” Nature Opinions Immunology, 2(6), 423-434. DOI: 10.1038/nri832
- Zhou, X., & Liao, W. (2018). “Regulatory T cells and their roles in the immune system.” Frontiers in Immunology, 9, 2456. DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.02456