Triple sugar iron agar (TSI) / TSIA Take a look at is a extremely versatile and indispensable instrument within the area of microbiology. With its skill to distinguish enteric micro organism primarily based on carbohydrate fermentation and hydrogen sulfide manufacturing, TSI performs an important position in bacterial identification, medical diagnostics, and analysis endeavors. This complete medium incorporates lactose, sucrose, glucose, ferrous sulfate, and phenol crimson, offering a wealthy substrate for assessing bacterial metabolic actions.
Precept of TSIA Take a look at
The precept underlying the Triple Sugar Iron (TSI) agar check revolves round its differential capabilities to discern between varied Gram-negative enteric pathogens primarily based on their metabolic actions. This medium incorporates three essential elements: triple sugars (lactose, sucrose, and glucose), a pH indicator (phenol crimson), and ferrous sulfate. Every part serves a selected function in facilitating the differentiation of bacterial strains.
Triple Sugars (Lactose, Sucrose, and Glucose):
These carbohydrates function substrates for bacterial fermentation. Micro organism with the enzymatic equipment to metabolize these sugars will make the most of them as vitality sources, resulting in the manufacturing of acidic byproducts. The utilization of various sugars produces attribute coloration modifications within the medium, aiding within the identification of metabolic capabilities.
pH Indicator (Phenol Crimson):
Phenol crimson acts as a pH indicator, altering coloration in response to alterations within the pH of the medium. Initially, the TSI agar seems reddish-orange, indicating a impartial pH. As micro organism ferment sugars and produce acidic byproducts, the pH of the medium decreases, inflicting phenol crimson to shift from yellow (acidic pH) to crimson (primary pH). This coloration change offers visible cues in regards to the fermentation patterns of the micro organism.
Ferrous Sulfate:
Ferrous sulfate serves a twin function within the TSI agar check. Firstly, it acts as a substrate for the detection of hydrogen sulfide (H2S) manufacturing by sure bacterial species. Micro organism able to decreasing sulfur compounds current within the medium produce hydrogen sulfide fuel, which reacts with ferrous sulfate to type a black precipitate of ferrous sulfide. This blackening of the medium serves as an indicator of H2S manufacturing. Secondly, ferrous sulfate additionally aids in detecting fuel manufacturing by micro organism. As fuel is produced throughout sugar fermentation, it might manifest as bubbles or fissures within the medium, offering extra diagnostic data.
By incorporating these elements into the TSI agar medium, microbiologists can exploit the metabolic range of enteric pathogens to distinguish between varied bacterial strains. The interpretation of TSI agar outcomes depends on observing coloration modifications, fuel manufacturing, and the formation of black precipitates, enabling microbiologists to make knowledgeable selections relating to bacterial identification and classification.
Deciphering TSIA Take a look at Outcomes:
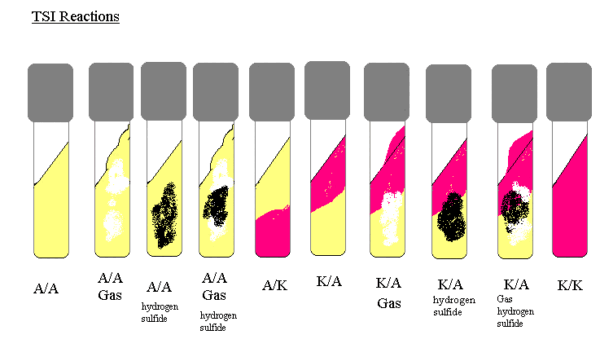
The interpretation of TSIA check outcomes entails cautious statement of coloration modifications and precipitate formations inside the medium. These observations present beneficial insights into bacterial metabolic profiles. The desk under outlines the interpretation of various TSI outcome combos:
| Outcome (slant/butt) | Image | Interpretation |
| Crimson/Yellow | Okay/A | Glucose fermentation solely, peptone catabolized. |
| Yellow/Yellow | A/A | Glucose and lactose and/or sucrose fermentation. |
| Crimson/Crimson | Okay/Okay | No fermentation, peptone catabolized. |
| Yellow/Yellow with bubbles | A/A,G | Glucose and lactose and/or sucrose fermentation, Fuel produced. |
| Crimson/Yellow with bubbles | Okay/A,G | Glucose fermentation solely, Fuel produced. |
| Crimson/Yellow with bubbles and black precipitate | Okay/A,G,H2S | Glucose fermentation solely, Fuel produced, H2S produced. |
| Yellow/Yellow with bubbles and black precipitate | A/A,G,H2S | Glucose and lactose and/or sucrose fermentation, Fuel produced, H2S produced. |
| Crimson/Yellow with black precipitate | Okay/A,H2S | Glucose fermentation solely, H2S produced. |
| Yellow/Yellow with black precipitate | A/A,H2S | Glucose and lactose and/or sucrose fermentation, H2S produced. |
Anticipated Outcomes and Examples of Micro organism in TSIA check:
- Crimson Slant/Yellow Butt (Okay/A):
- Instance Micro organism: Citrobacter freundii, Citrobacter koseri, Morganella morganii.
- Yellow Slant/Yellow Butt (A/A):
- Instance Micro organism: Escherichia coli, Enterobacter aerogenes, Klebsiella oxytoca.
- Crimson Slant/Crimson Butt (Okay/Okay):
- Instance Micro organism: Acinetobacter spp., Pseudomonas spp.
- Yellow Slant/Crimson Butt with Fuel (A/A, G):
- Instance Micro organism: Escherichia coli, Enterobacter aerogenes, Klebsiella pneumoniae.
- Crimson Slant/Yellow Butt with Fuel and Black Precipitate (Okay/A, G, H2S):
- Instance Micro organism: Citrobacter freundii, Proteus mirabilis.
- Yellow Slant/Yellow Butt with Fuel and Black Precipitate (A/A, G, H2S):
- Instance Micro organism: Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris.
- Crimson Slant/Yellow Butt with Black Precipitate (Okay/A, H2S):
- Instance Micro organism: Citrobacter freundii, Salmonella spp.
- Yellow Slant/Yellow Butt with Black Precipitate (A/A, H2S):
- Instance Micro organism: Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris.
Distinctive Options of TSI Outcomes:
- Shade Modifications: Point out the utilization of particular sugars and pH alterations.
- Fuel Manufacturing: Manifests as bubbles or cracks within the agar medium.
- H2S Manufacturing: Results in a black precipitate formation within the medium.
Sensible Issues:
- Incubate TSI tubes at 37°C for 18-24 hours for optimum outcomes.
- Extended incubation might distort interpretations, affecting outcome reliability.
TSIA Recipe:
Substances:
- Pancreatic digest of casein USP: 10.0 g
- Peptic digest of animal tissue USP: 10.0 g
- Glucose: 1.0 g
- Lactose: 10.0 g
- Sucrose: 10.0 g
- Ferrous sulfate or ferrous ammonium sulfate: 0.2 g
- Sodium chloride (NaCl): 5.0 g
- Sodium thiosulfate: 0.3 g
- Phenol crimson: 0.024 g
- Agar: 13.0 g
- Distilled water: 1,000 mL
Directions:
- Combine all components in distilled water.
- Regulate pH to 7.3.
- Boil till dissolved.
- Sterilize by autoclaving at 121°C for quarter-hour.
- Cool and dispense into tubes with slanted place.
- Solidify to be used in bacterial tradition.
Storage: Hold in cool, dry place away from daylight.
This recipe creates TSIA agar, facilitating detection of carbohydrate fermentation and H2S manufacturing in micro organism, aiding in microbial identification.
Significance of TSIA check in Microbiological Diagnostics and Analysis:
The Triple Sugar Iron agar check holds immense significance in microbiological diagnostics and analysis for a number of causes:
- Bacterial Identification: TSI permits the differentiation of bacterial strains primarily based on their metabolic capabilities, aiding in bacterial identification and classification.
- Scientific Relevance: TSI outcomes inform medical interventions, notably in diagnosing gastrointestinal infections brought on by enteric micro organism, guiding therapy methods and stopping illness unfold.
- Microbial Ecology Research: TSI agar check is instrumental in microbial ecology research, offering insights into the range and metabolic actions of bacterial communities in several environments.
- Analysis Instrument: TSI agar check serves as a beneficial analysis instrument for finding out bacterial metabolism, adaptation mechanisms, and virulence components, contributing to our understanding of bacterial physiology.
- High quality Management: TSI agar check is used for high quality management functions in medical and industrial settings, guaranteeing the purity and security of assorted merchandise by detecting potential enteric pathogens.
Conclusion:
In abstract, the Triple Sugar Iron agar check stands as a cornerstone method in microbiology, providing beneficial insights into bacterial metabolic profiles and aiding in bacterial identification, medical diagnostics, and analysis endeavors. By meticulous interpretation and adherence to greatest practices, TSI agar check continues to play a pivotal position in advancing our understanding of microbial communities and their implications for human well being.
Study Extra;