Volcanoes on Venus Would possibly Be Erupting Proper Now
Scientists have discovered indicators of contemporary flowing lava on Venus in decades-old information from NASA’s Magellan spacecraft
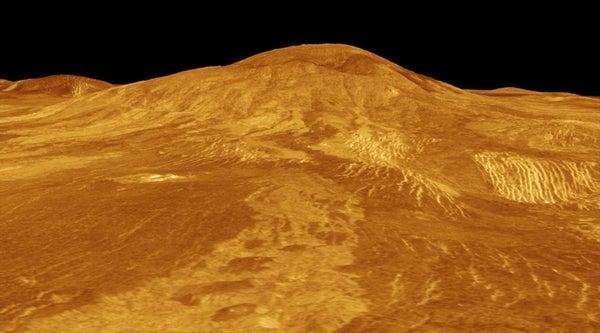
A pc-simulated view of Sif Mons.
Proof continues to assemble that Venus is extra geologically energetic than beforehand thought.
Planetary scientists scouring decades-old information from NASA’s Magellan spacecraft have discovered indicators of lava flows coming from two volcanoes on Venus that erupted within the early Nineteen Nineties. That was when Magellan orbited the hellish world overhead.
This marks the second time scientists have recognized direct geological proof of current volcanic exercise on Venus, suggesting the planet might be as geologically energetic as Earth, with volcanoes probably spewing on its floor as you learn this.
On supporting science journalism
In case you’re having fun with this text, think about supporting our award-winning journalism by subscribing. By buying a subscription you’re serving to to make sure the way forward for impactful tales concerning the discoveries and concepts shaping our world right this moment.
Venus and Earth are practically the identical measurement and had been showered with equal quantities of water billions of years in the past. For that reason, many scientists marvel why Venus changed into a hellscape whereas our planet bloomed right into a liveable orb. Learning Venus’ volcanic exercise, which scientists suspect is pushed by inner warmth, might supply a window into the evolution of each planets.
The newly noticed lava flows seem to have oozed out from the western slopes of Sif Mons, an enormous protect volcano, and Niobe Planitia, a comparatively flat area house to many volcanoes. By referencing lava flows on Earth, scientists estimate Sif Mons’ eruption poured about 12 sq. miles (30 sq. kilometers) of rock, which is ample to fill 36,000 Olympic swimming swimming pools. The Niobe Planitia eruption blasted lava that would fill 54,000 Olympic swimming pools, NASA mentioned in an announcement. To place that into context, nevertheless, the 2022 eruption of Mauna Loa in Hawaii — Earth’s largest energetic volcano — spouted sufficient lava to fill 100,000 Olympic swimming pools.
Proof for the newfound lava flows is rooted in radio waves beamed at Venus through Magellan’s radar. These waves zipped by means of the planet’s thick, poisonous clouds earlier than bouncing off the world’s floor and returning again to the spacecraft. These reflections, referred to as backscatter, can ferry details about a planet’s rocky floor.
Whereas analyzing Magellan’s information gathered between 1990 and 1992, scientists discovered the sign energy had elevated throughout later orbits. They interpret the spike as vivid, freshly fashioned rocks on the floor — that are probably solidified lava.
“We interpret these signals as flows along slopes or volcanic plains that can deviate around obstacles such as shield volcanoes like a fluid,” examine co-author Marco Mastrogiuseppe of Sapienza College of Rome mentioned in an announcement. “After ruling out other possibilities, we confirmed our best interpretation is that these are new lava flows.”
The newly recognized lava flows seem vivid in radar information, which might imply they’re younger and thus not but eroded. Alternatively, these outcomes might additionally imply the lava is rougher than its older, smoother environment, examine lead creator Davide Sulcanese of the Università d’Annunzio in Pescara in Italy informed Sky & Telescope.
The findings construct on final 12 months’s historic discovery of an altered vent of the volcano Maat Mons close to Venus’ equator, which appeared to have modified form and grown noticeably bigger over eight months, probably as a consequence of an eruption-triggered collapse.
“This exciting work provides another example of volcanic change on Venus from new lava flows that augments the vent change Dr. Robert Herrick and I reported last year,” examine co-author Scott Hensley, a senior analysis scientist on the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California, mentioned in an announcement. “This result, in tandem with the earlier discovery of present-day geologic activity, increases the excitement in the planetary science community for future missions to Venus.”
This analysis is described in a paper revealed Monday (Could 27) within the journal Nature Astronomy.
Copyright 2024 Area.com, a Future firm. All rights reserved. This materials might not be revealed, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.