We lastly know what introduced gentle to the darkish and formless void of the early Universe.
In keeping with knowledge from the Hubble and James Webb House Telescopes, the origins of the free-flying photons within the early cosmic daybreak had been small dwarf galaxies that flared to life, clearing the fog of murky hydrogen that crammed intergalactic house. A brand new paper in regards to the analysis was revealed in February.
“This discovery unveils the crucial role played by ultra-faint galaxies in the early Universe’s evolution,” stated astrophysicist Iryna Chemerynska of the Institut d’Astrophysique de Paris.
“They produce ionizing photons that transform neutral hydrogen into ionized plasma during cosmic reionization. It highlights the importance of understanding low-mass galaxies in shaping the Universe’s history.”
Firstly of the Universe, inside minutes of the Massive Bang, house was crammed with a scorching, dense fog of ionized plasma. What little gentle there was would not have penetrated this fog; photons would merely have scattered off the free electrons floating round, successfully making the Universe darkish.
Because the Universe cooled, after about 300,000 years, protons and electrons started to come back collectively to kind impartial hydrogen (and a bit of little bit of helium) gasoline.
Most wavelengths of sunshine may penetrate this impartial medium, however there was little or no in the best way of sunshine sources to provide it. However from this hydrogen and helium, the primary stars had been born.
These first stars delivered radiation that was sturdy sufficient to peel electrons away from their nuclei and reionize the gasoline. By this level, nonetheless, the Universe had expanded a lot that the gasoline was diffuse, and couldn’t forestall gentle from shining out.
By about 1 billion years after the Massive Bang, the top of the interval referred to as the cosmic daybreak, the Universe was solely reionized. Ta-da! The lights had been on.
However as a result of there’s a lot murk within the cosmic daybreak, and since it is so dim and much away throughout time and house, we have had hassle seeing what’s there.
Scientists thought that the sources chargeable for a lot of the clearing will need to have been highly effective – enormous black holes whose accretion produces blazing gentle, for instance, and huge galaxies within the throes of star formation (child stars produce plenty of UV gentle).
JWST was designed, partly, to see into the cosmic daybreak and attempt to see what lurks therein. It has been very profitable, revealing all kinds of surprises about this significant time within the formation of our Universe. Surprisingly, the telescope’s observations now counsel that dwarf galaxies are the important thing participant in reionization.
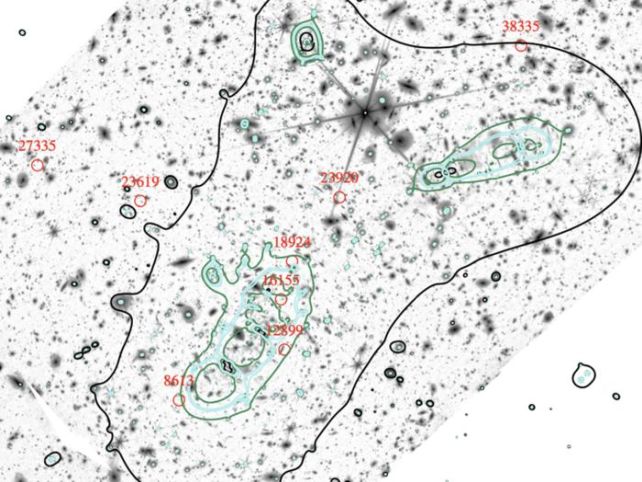
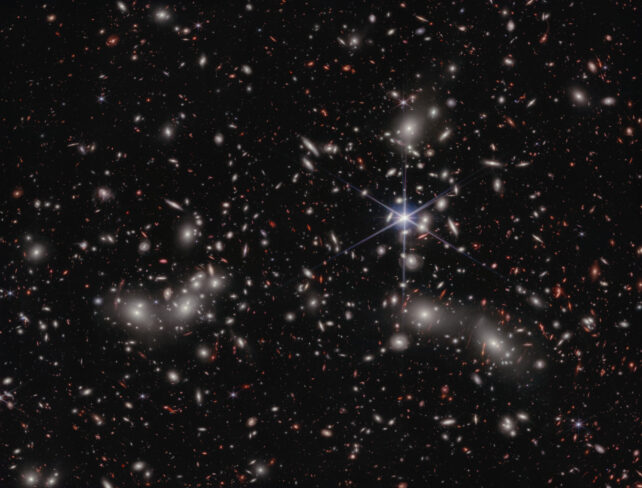
A world workforce led by astrophysicist Hakim Atek of the Institut d’Astrophysique de Paris turned to JWST knowledge on a galaxy cluster referred to as Abell 2744, backed up by knowledge from Hubble.
Abell 2744 is so dense that space-time warps round it, forming a cosmic lens; any distant gentle touring to us by means of that space-time turns into magnified. This allowed the researchers to see tiny dwarf galaxies near the cosmic daybreak.
Then, they used JWST to acquire detailed spectra of those tiny galaxies. Their evaluation revealed that, not solely are these dwarf galaxies probably the most considerable galaxy sort within the early Universe, they’re far brighter than anticipated.
The truth is, the workforce’s analysis exhibits that dwarf galaxies outnumber giant galaxies by 100 to 1, and their collective output is 4 instances the ionizing radiation often assumed for bigger galaxies.
“These cosmic powerhouses collectively emit more than enough energy to get the job done,” Atek stated.
“Despite their tiny size, these low-mass galaxies are prolific producers of energetic radiation, and their abundance during this period is so substantial that their collective influence can transform the entire state of the Universe.”

It is one of the best proof but for the power behind reionization, however there’s extra work to be performed. The researchers checked out one small patch of the sky; they should guarantee that their pattern is not simply an anomalous cluster of dwarf galaxies, however is a consultant pattern of the whole inhabitants within the cosmic daybreak.
They intend to check extra cosmic lens areas of the sky to acquire a wider pattern of early galactic populations. However simply on this one pattern, the outcomes are extremely thrilling. Scientists have been chasing solutions on reionization for as lengthy we have recognized about it. We’re on the point of lastly blowing away the fog.
“We have now entered uncharted territory with the JWST,” stated astrophysicist Themiya Nanayakkara of Swinburne College of Know-how in Australia.
“This work opens up more exciting questions that we need to answer in our efforts to chart the evolutionary history of our beginnings.”
The analysis has been revealed in Nature.
A model of this text was initially revealed in March 2024.